In this article, we’re going to look at one of the most overlooked business models in tech. A model that many founders don’t know about, and some use without even knowing it.
Let’s dive into the B2B2C model.
The two business models that are most familiar and that companies have historically relied on are business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C). But there is another model that you might have come across called business to business to consumer (B2B2C).
This is a less well-known and often misunderstood model in the business world, which has a slightly more complex supply chain.
In this guide, we will be giving you a complete overview of the B2B2C model by taking a deep dive into the following:
🔹 What exactly is B2B2C?
🔹 What does a B2B2C relationship look like?
🔹 Examples of B2B2C businesses.
🔹 Benefits of the B2B2C business model.
🔹 Challenges of the B2B2C business model.
🔹 What is needed for a successful B2B2C partnership?
What Is B2B2C?

B2B2C is a business model used by companies to gain access to the existing customer base of another business by partnering with them.
To better understand exactly how this business model works, let’s first look at how the two more common business models work: the B2B and B2C models.
B2B Business Model Defined
The B2B (business to business) model involves transactions between companies rather than between a company and the consumer market.
A typical example would be the relationship between a wholesaler and a retailer. The wholesaler does not sell directly to the consumer but instead only does business with retailers, who then sell the product they purchased from the wholesaler to the consumer.
In software, Salesforce, Xero, and Hubspot are all classic examples of B2B products.
B2C Business Model Defined
The business-to-consumer model involves a company selling products or services directly to consumers.
Take pet portraits as an example. Doggovinci sells personalised pet portraits to its consumers, who visit the website and order from the company directly.

B2B2C Business Model Defined
The B2B2C model is a blend. It involves a company partnering with another business to sell products or services directly to the clients within the consumer base of the partner business.
An example of this model would be a delivery service like Uber Eats.
Uber Eats partners with restaurants to sell their delivery service to the customers of those restaurants. However, the customers know that even though they are buying the products of a specific restaurant, they are buying them from Uber Eats.
Uber Eats owns the customer relationship and can sell the products of multiple restaurants on its platform, thereby growing its client base by selling its delivery services to the clients of various restaurants.
How Does the B2B2C Business Model Work?

Let’s map out exactly what a B2B2C arrangement looks like between three parties: Business A, Business B, and the consumer.
Business A is a popular local restaurant that wants to increase sales by offering delivery of its food to existing and new customers. However, they do not want to hire additional employees to act as delivery drivers.
Business B is a food delivery service like Uber Eats, which makes revenue by charging a fee to the consumer when delivering food to them. So Business B solves a problem for Business A, which is why Business A will allow it to sell its delivery service to its customer base.
In this scenario, Business B owns the customer relationship, as the customer is paying them both for food and delivery. The customer knows that it is getting the food from Business A (which either sells the food to Business B or gives it to them on consignment), and they also know they are buying delivery from Business B.
B2B2C Examples
Delivery services like Uber Eats are good examples of a B2B2C model, but there are several other examples of this model.
E-commerce Dropshipping Stores
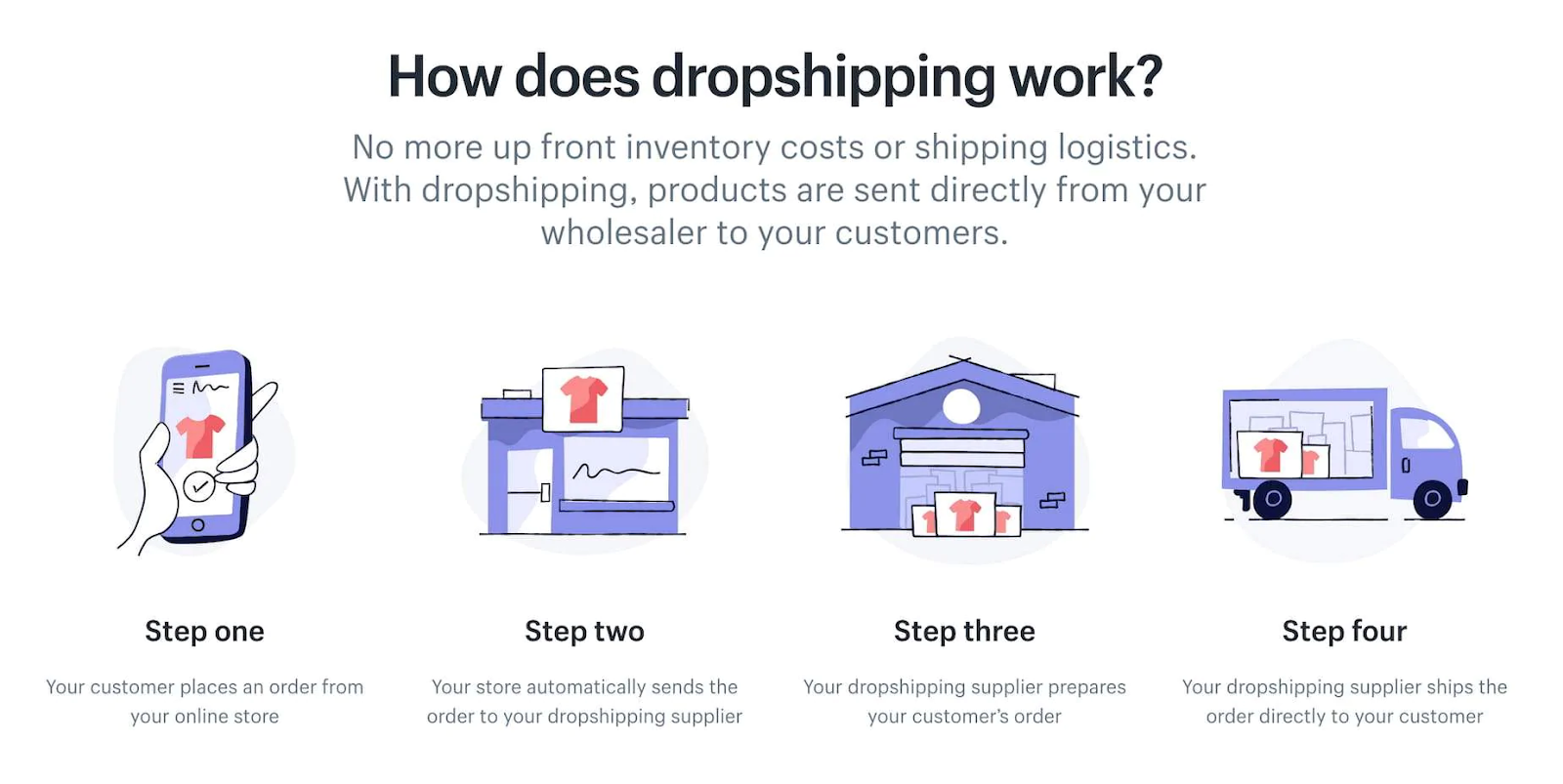
One of the most common examples of a B2B2C model is a dropshipping business.
This model involves setting up an e-commerce website where your business sells the products of your suppliers directly to your consumers, but your suppliers fulfil the orders.
You don’t keep any stock yourself, but when a client places an order with you, you then place an order with the appropriate supplier, who then ships it directly to your client.
The B2B relationship is between you and your supplier, and the B2C relationship is between you and your e-commerce clients.
Online Reservation Sites

Another good example of a B2B2C model is an online reservation site like OpenTable.
With this model customers use the service of OpenTable to find restaurants and book a table.
OpenTable owns the customer relationship and can sell its booking service directly to the customers of the restaurants listed on its site.
Online Retailers

Probably the most well-known example of a company using the B2B2C model is Amazon.
Amazon offers an online marketplace for its customers where they can buy almost any product, but most of those products are not manufactured by Amazon.
Instead, companies partner with Amazon to sell their products on their platform.
Amazon owns the client relationship, as consumers are buying from Amazon, and Amazon can sell the products of multiple companies within its store using a B2B2C model.
Benefits of the B2B2C Business Model

Companies might think that it would be better for them to sell their products directly to their end users themselves, but there are a lot of benefits for all partners with a B2B2C relationship.
Let’s have a look at some of the main benefits.
Growth Potential
One of the main reasons why businesses enter into B2B2C partnerships is to expand their potential for economic growth and to increase their potential customer base.
Businesses typically enter a B2B2C relationship because it offers them opportunities to increase their revenue by leveraging the services, customer base, logistics, and brand credibility of the other business.
Take our example of a delivery business partnering with a restaurant chain to provide delivery services to its customers. This B2B2C partnership increases revenue for both parties as the restaurant gets the opportunity to sell more food, and the delivery business gets more inventory to attract more customers.
Overhead Cost Reduction
A B2B2C relationship can reduce the operational and overhead costs for both parties.
For example, with an e-commerce dropshipping store, the owner of the e-commerce website does not have to stock any products or ship them, thereby eliminating warehouse and shipment costs.
And the supplier does not have to deal directly with consumers, so this eliminates any costs involved with customer service and sales.
This allows both businesses to specialise in areas of core strength.
Control of Branding and Pricing
With a B2B2C model, companies can retain control over branding and pricing.
In a traditional B2B model, a manufacturer might not be able to dictate to a retail store the price at which it should sell its products. Similarly, if a company white-labels its product or service to a reseller they lose the advantage of having end users recognise its brand.
But in a B2B2C relationship, a company can retain control of both.
For example, restaurants having their food delivered by a food delivery service can still set their prices for their food, and they can ensure that the food being delivered is manufactured to the standard that their customers expect.
Credibility
Entering into a B2B2C relationship can allow one party to leverage the brand recognition and credibility of the other.
For example, a small business without brand recognition can partner with an online marketplace like Amazon.
Consumers know and trust the Amazon brand. They might be more willing to buy products from a business they do not know via Amazon than buying directly from the business itself.
Challenges of the B2B2C Business Model

Although there are many benefits to using a B2B2C model, there are challenges involved as well.
Let’s look at some of the most common ones.
Complex Partnerships
A B2B2C partnership involves more stakeholders than a traditional B2B or B2C model, which leads to more complexity.
In a B2B2C model, businesses need to manage their relationships with their partners as well as with their end customers. This means they have to balance their partner’s needs with the needs and expectations of their consumers.
Customer Experience
The B2B2C introduces a middleman into the supply chain, taking the interaction with clients out of the hands of the business that is not providing the service to its customers.
For example, a restaurant does not have control over the level of customer service provided by a delivery service delivering its food to its customers.
This means that a business must consider customer expectations and whether it will be beneficial to use the partner to provide that service or not.
Customer Ownership
As we have seen, this is one of the main differences between a B2B2C model and a traditional B2B model, namely that the company providing a service to the customer base of another company ends up owning or co-owning the customer relationship with the end-user.
Whilst this is not necessarily a bad thing, it can be a risk to not have control over the client relationship.
For example, if a restaurant decides that it no longer wants to use a delivery service, but rather bring delivery in-house, it does not have direct access to the customer base of the delivery service it was using.
Conclusion
Even though a B2B2C model doesn’t work for every business idea and it can be more complex than traditional B2B or B2C models, it can have many advantages, such as gaining access to a larger customer base and providing your clients with services you might not otherwise have been able to.
MOHARA is a product venture studio with over ten years of experience in developing software solutions. We have worked with companies such as Diageo to implement their business idea utilising a B2B2C model.
If you’re a startup founder with a business idea that would benefit from a B2B2C model, why not get in touch and see how we can help?